Understanding the Holistic Approach to Care: A Comprehensive Exploration
In the realm of health care, the holistic approach has emerged as a prominent paradigm, offering a framework that seeks to address the multifaceted dimensions of human well-being. This model recognizes that health is not merely the absence of disease but encompasses a harmonious balance between physical, emotional, social, and spiritual facets of life. The essence of holistic care lies in its intrinsic ability to treat the individual as a whole, rather than isolating symptoms or conditions. This examination endeavors to elucidate the constituents, advantages, and implications of adopting a holistic perspective in health care practices.
Defining Holistic Care: A Multifaceted Perspective
Holistic care is characterized by its integrative methodology, wherein health care providers strive to understand the individual’s needs through a comprehensive lens. Central to this approach is the belief that the sum of a person’s experiences, their environment, and their internal narratives profoundly influence their health outcomes. Holistic care encompasses several core components:
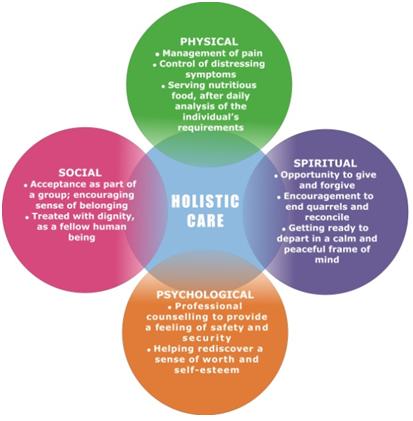
Physical Well-Being: The physical dimension remains crucial, as it includes the diagnosis and management of health conditions. However, holistic care transcends the mere treatment of ailments, promoting overall fitness and vitality through nutrition, exercise, and preventive strategies.
Emotional and Psychological Health: Recognizing the profound impact that emotional states have on physical health, holistic care emphasizes mental well-being. Techniques such as mindfulness, counseling, and therapy play a vital role in fostering resilience, coping strategies, and self-awareness among patients.
Social Connections: The importance of social health cannot be overstated. A supportive network of family, friends, and community can significantly bolster an individual’s ability to navigate health challenges. Holistic care advocates for strengthening these bonds, thereby promoting a sense of belonging and purpose.
Spiritual Dimensions: The spiritual aspect of holistic care addresses the search for meaning and connectedness beyond the physical world. Whether through traditional religious practices or personal spiritual beliefs, fostering this aspect can enhance overall well-being and provide individuals with a greater sense of peace.
The Ethical Implications of Holistic Care
Woven into the fabric of holistic care are profound ethical considerations that challenge conventional medical practices. Central to these ethical discussions is the concept of patient autonomy and empowerment. A holistic model necessitates active participation from patients in their health decisions. This paradigm shift acknowledges individuals as experts in their experiences, thereby fostering dialogue that respects their values, preferences, and needs.
Culturally Sensitive Approaches: One vital ethical consideration is the recognition of cultural diversity in health care. Holistic care emphasizes culturally competent practices that promote inclusivity and respect for varied belief systems. Health care providers must engage in ongoing education to understand cultural nuances effectively and implement interventions that resonate with diverse populations.
Integrative Treatment Modalities: Emerging from the holistic framework is the balance between conventional and alternative therapies. The ethical commitment to harm reduction compels practitioners to explore all viable treatment avenues, thus broadening the scope of care available to patients. Integration of modalities—such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and yoga—requires a critical appraisal of evidence while holding to the ethical principles of beneficence and non-maleficence.
Addressing Health Disparities: A fundamental ethical obligation of holistic care is the commitment to address social determinants of health. Systemic barriers often impede marginalized populations from accessing comprehensive care. Health care systems must strive to create equitable opportunities, recognizing that social injustices perpetuate health disparities. A holistic perspective advocates for institutional reform and challenges the status quo, asserting that care should not privilege certain demographics over others.
Advances in Holistic Practices: A Review of Contemporary Trends
In recent years, the holistic approach has gained traction within health systems as a response to the limitations of conventional medicine. An increasing acknowledgment of the biopsychosocial model of health has facilitated the integration of holistic practices into mainstream care.
Patient-Centered Care: This modern evolution emphasizes personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs and preferences. It amalgamates clinical knowledge with patient experiences, thereby ensuring that health care is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. As a result, practitioners cultivate therapeutic relationships that inspire trust and collaboration.
Technological Innovations: The rise of telemedicine and digital health tools has revolutionized the delivery of holistic care. Virtual platforms enable health care providers to offer remote support for mental well-being, nutritional counseling, and even mindfulness coaching. This accessibility fosters a sense of continuity and engagement essential for holistic treatment.
Community-Based Initiatives: Programs such as wellness workshops, mindfulness retreats, and support groups embody the essence of holistic care. These initiatives often empower individuals with knowledge and resources to navigate their health journeys proactively. By building community resilience, these programs encourage collective well-being and instill a sense of agency among participants.
Challenges and Future Directions of Holistic Care
Despite the growing recognition of holistic care, several challenges persist that inhibit its widespread application within health care settings. Resistance to change from entrenched medical paradigms remains a significant hurdle. Advocating for holistic practices necessitates the dismantling of longstanding hierarchies and the fostering of interdisciplinary collaboration among health professionals.
Another challenge is the imperative for robust empirical evidence that substantiates the efficacy of holistic interventions. Research funding must prioritize studies exploring the long-term impact of holistic care modalities. Enhanced data collection methods and outcome measures will illuminate the benefits of this integrative approach and bolster its credibility in the eyes of skeptics.
Looking ahead, there is a pressing need for policy frameworks that embrace holistic care as a fundamental aspect of health service delivery. This shift entails recognition at institutional levels of the interconnection between emotional, social, and physical health. Advocacy for reform must persist to ensure that holistic approaches are not relegated to the periphery but are woven into the very core of health care systems.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Future in Health Care
The holistic approach to care represents a vital movement towards comprehensive health that transcends mere symptom management. It calls for a reevaluation of individual health experiences and recognizes the myriad of factors influencing well-being. By fostering inclusivity, prioritizing ethical considerations, and embracing advancements, the holistic paradigm has the potential to reshape health care in profoundly meaningful ways. The journey ahead requires dedication, collaboration, and a commitment to addressing the inherent disparities within health systems. Only then can we truly foster an environment that champions holistic well-being for all individuals.