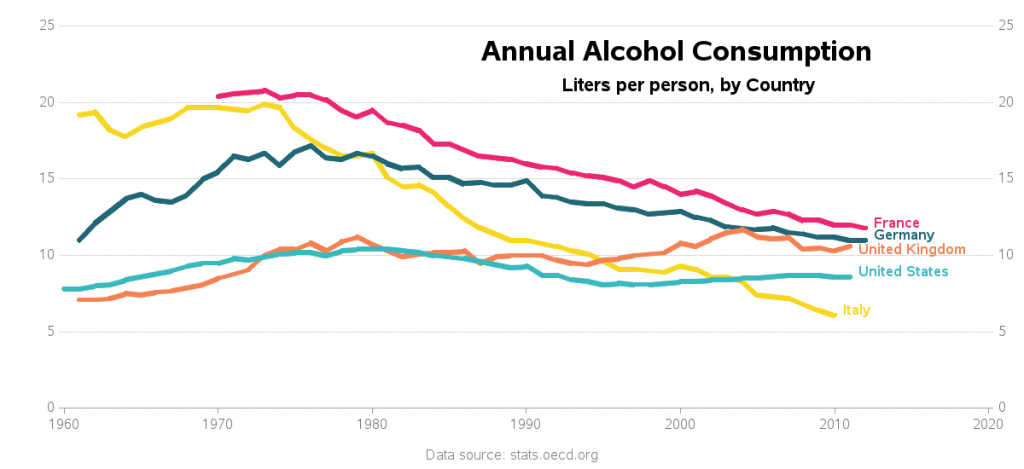
Alcohol consumption serves as a cultural lens through which societal norms, health implications, and debates about personal responsibility can be examined. Analyzing the differences in drinking habits between the United States and Italy uncovers deeper issues regarding lifestyle choices, societal expectations, and historical context. This exploration should compel the reader to reflect critically on the implications of these differences, challenging common assumptions about alcohol consumption.
The United States and Italy represent two distinctly divergent approaches to alcohol consumption. The erstwhile perception; that Italians, with their wine-centric culture, are irrevocably more indulgent than their American counterparts, merits scrutiny. As we peel back the layers of cultural attitudes surrounding alcohol, it becomes clear that a nuanced analysis is necessary to appreciate the full scope of this topic.
Examining the quantitative aspects of alcohol consumption reveals stark contrasts. In Italy, the average yearly alcohol consumption per capita encapsulates a European trend that largely embraces moderate drinking. The Mediterranean diet, often championed for its health benefits, allocates a space for wine, generally consumed in smaller quantities with meals. Conversely, the United States presents a different narrative, where binge drinking and a burgeoning cocktail culture dominate the scene. This discrepancy indicates a broader cultural ethos—one that signifies not merely preferences, but foundational views on alcohol itself.
In delving into the sociocultural implications of alcohol consumption in these two nations, we confront the question: How does one’s environment shape their relationship with alcohol?
The Cultural Paradigm: Perceptions of Alcohol
In Italy, wine is ingested as an integral element of daily life; it is commonly enjoyed during family meals and social gatherings. The act of drinking wine transforms from mere consumption into a social ritual, rich with historical roots and family traditions. This cultural context fosters a responsible attitude towards alcohol, where moderation is encouraged, and excess is often viewed with disfavor. Drinking to enjoy is celebrated—excessive drinking, however, is not.
In contrast, American culture has largely romanticized binge drinking, especially among younger demographics. Social events in the U.S. frequently associate alcohol with celebration, whereby usage often escalates into excess. The emergence of beer pong tournaments and fervent nightlife scenes illustrates not just a consumption pattern, but a deeper societal acceptance of intoxication as a mode of social expression. This stark dichotomy among cultures invites critical reflection: is alcohol merely a means of enjoyment, or does it symbolize deeper psychological or emotional dependencies?
Rethinking Health: Implications of Consumption Patterns
The health implications of these differing drinking habits warrant extensive investigation. Research consistently highlights the cardiovascular benefits associated with moderate wine consumption endemic to the Mediterranean diet. Conversely, the prevalence of alcohol-related disorders in the United States raises pressing public health concerns. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports alarming trends in alcohol abuse, underscoring the ramifications of excessive consumption on both physical health and societal well-being. The resulting societal costs—spanning healthcare expenditures, lost productivity, and familial disruptions—pose challenging questions that demand collective action.
To address the public health crisis tied to excessive drinking in the U.S., it becomes imperative to examine existing educational programs and prevention strategies. Advocates for change often argue that many prohibition-style initiatives fall short, ignoring the cultural complexity and social pressures surrounding drinking. Instead, frameworks that draw upon Italian models of moderation may yield favorable outcomes. Comprehensive programs that focus on responsible enjoyment may desensitize the stigma around drinking while simultaneously elevating awareness regarding the risks associated with excessive consumption.
Gender Perspectives: The Role of Women in Alcohol Consumption
The variance between the two nations extends beyond mere numbers; it bleeds into the gendered narratives surrounding drinking behavior. Traditionally, Italian women possess a significant role within family structures, where culinary practices often include wine during meals. This participation normalizes alcohol as a communal rather than individualistic pursuit. In Italy, the stigma often associated with women and drinking is less pronounced, allowing for a more equitable engagement with alcohol.
Conversely, in the U.S., issues of gender and alcohol consumption reveal a disquieting trend. The societal pressure, especially surrounding college culture, amplifies the narrative that youthful women must participate in drinking rituals to achieve acceptance among peers. Yet, increased awareness of addiction among women provides an opportunity to rethink these constructs. Female-specific outreach programs and resources could catalyze a paradigm shift, dismantling preconceived notions surrounding gender and drinking while fostering an understanding that embraces moderation.
Confronting the Myths: Stereotypes and Realities
Challenging stereotypes surrounding both American and Italian drinking habits is vital. The overly simplistic characterization of Italians as ‘wine-drinking socialites’ often overlooks the nuances of family influence and community-based consumption. It is critical to approach the issue with a balanced lens, understanding that binge drinking—whether in Italy or the U.S.—is a concern that plagues various segments of society.
Similarly, the American tendency toward binge drinking must not overshadow the significant movements advocating for sobriety and wellness within the nation. Social media campaigns promoting moderation and celebrating sober lifestyles are gaining traction, indicating a shift toward a healthier relationship with alcohol. Recognizing that the journey toward responsible drinking is not confined to geographical boundaries is essential in cultivating a broader, inclusive dialogue around alcohol dependence.
The Role of Policy and Regulation
Policy measures play a crucial role in shaping drinking cultures and behaviors within each nation. Italy’s approach toward alcohol regulation leans towards liberal policies, entwined with cultural norms that value moderation and social responsibility. In sharp contrast, the United States remains entrenched in a complex web of restrictive laws, state interventions, and rigorous enforcement protocols that often fail to mitigate the alcohol-related crises faced nationwide.
To move towards a more responsible drinking culture, it may be beneficial to draw inspiration from the Italian model. A shift towards regulation that emphasizes education rather than restriction could forge a path to healthier relationships with alcohol. Fostering community dialogues, creative public health campaigns, and innovative educational initiatives are essential steps in this transformative journey.
Concluding Reflections: A Collective Responsibility
As we probe the chasm dividing U.S. and Italian drinking habits, it becomes apparent that tackling alcohol consumption extends beyond mere statistics and enjoyment. It is an invitation to reconsider what we value within our respective societies. The onus rests on us to foster cultures that embrace moderation, celebrate responsible consumption, and advocate for informed, health-conscious attitudes towards alcohol. This challenge inevitably compels the reader to reflect: Are we merely passive observers of our drinking culture, or will we choose to engage actively in shaping its future?