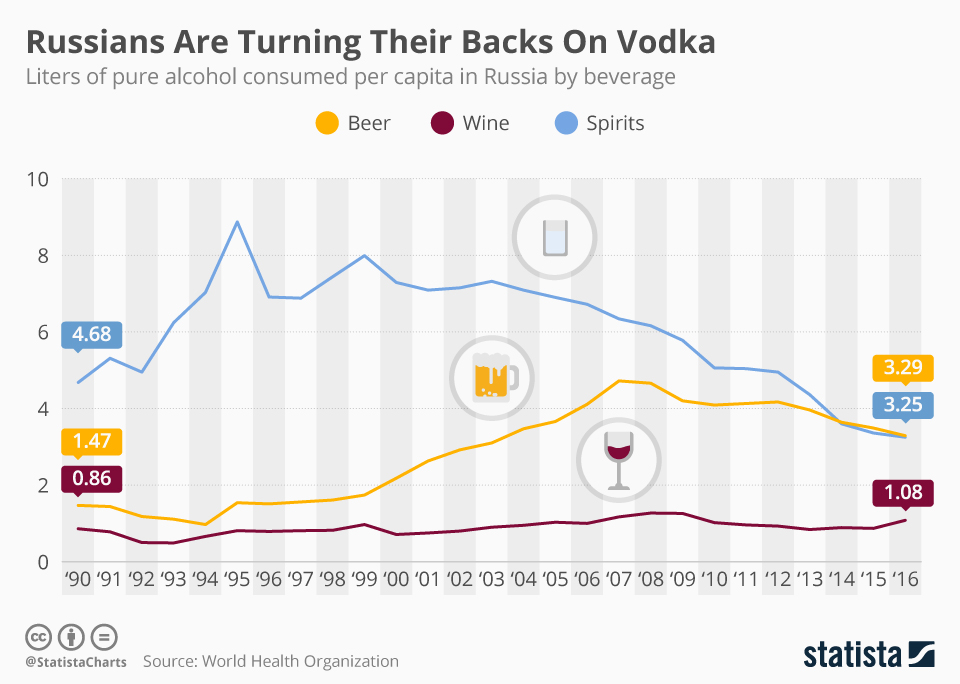
Alcohol consumption in Russia is a deeply entrenched aspect of the socio-cultural fabric, historically characterized by a myriad of factors ranging from tradition to socio-economic conditions. This article aims to explore the evolving dynamics of alcohol consumption in Russia while examining recent trends that promise a transformative shift in both habits and attitudes towards alcoholic beverages, particularly vodka, which has long been regarded as a national emblem.
In recent years, notable shifts in the landscape of alcohol consumption have emerged. An increasing number of Russians are reevaluating their relationship with alcohol, which begs the question: what influences this metamorphosis, and what does it signify for Russian society at large?
Considering the implications of these changes paves the way for a more profound understanding of contemporary Russian identity.
Historical Context: The Roots of Alcohol Culture
The history of alcohol consumption in Russia dates back centuries, with various beverages—including mead, beer, and notably vodka—being woven into the cultural and social ethos. Vodka has often played a pivotal role in both celebratory and ritualistic practices. The beverage is emblematic of hospitality and represents a means of forging social bonds among friends and family.
However, this association with conviviality is intricately overshadowed by the detrimental social ramifications of excessive consumption. The late Soviet period witnessed alarming statistics of alcohol-related deaths and social disarray linked to heavy drinking behaviors, with vodka consumption reaching unprecedented levels.
Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, a marked increase in the availability and marketing of alcoholic beverages exacerbated the situation, leading to a public health crisis. The post-Soviet era heralded a period characterized by rampant consumption, resulting in significant demographic challenges, including abysmal life expectancy rates among men.
Legislative efforts were implemented to curtail the rampant drinking culture, with restrictions on sales and marketing of alcohol. These measures were aimed at mitigating the health impacts associated with high levels of consumption and fostering a healthier populace.
Recently, there has been an emergence of public campaigns aimed at shifting public perception of alcohol, fostering a climate of health consciousness. As such, understanding the socio-economic and cultural nuances is vital to interpreting the evolving landscape of alcohol consumption in Russia.
Changing Attitudes: The New Wave of Alcohol Consumption
In light of these ongoing transformations, contemporary society witnesses a refreshing rejection of excessive drinking habits among younger generations. This demographic seeks to redefine social practices that have until now circumscribed their leisure activities. The willingness to embrace moderation and abstain from heavy drinking serves as a striking departure from the historical norms that have long dictated Russian drinking culture.
Social media plays a fundamental role in this transformation, as platforms embrace narratives that promote wellness and creative forms of social interaction devoid of excessive alcohol. The rise of influencers advocating for sobriety and mental well-being stands testament to the shifting paradigm. These narratives resonate with youth seeking empowerment through healthier lifestyles.
Moreover, a burgeoning demand for non-alcoholic alternatives reflects the burgeoning consciousness around health and wellness. The proliferation of low-alcohol and non-alcoholic beverages has emerged as a lucrative market sector, catering to a populace increasingly cognizant of the health risks associated with excessive drinking.
Furthermore, the growth of lifestyle brands centered on mindfulness and conscious living reflects a broader cultural shift. This affluence of choices allows individuals to redefine social gatherings, making them more inclusive while breaking the stigma surrounding sobriety.
Public Health Implications: Toward a Healthier Future
The ongoing reevaluation of alcohol consumption is intimately tied to public health improvements. Alarmingly high rates of alcohol-related morbidity and mortality have necessitated a decisive reevaluation of consumption patterns. By promoting healthier lifestyles and reducing heavy drinking culture, society can begin to address the chronic public health crisis stemming from excessive alcohol consumption.
Global interest in Russia’s alcohol consumption patterns has been piqued by the remarkable health consequences associated with heavy drinking. However, the positive trends indicating a decline in consumption are promising, particularly as the government and health organizations implement programs aimed at informing the public about the risks of drinking.
Awareness initiatives emphasizing responsible drinking, the dangers of binge drinking, and the importance of mental health bolster a broader movement toward healthier societal norms. As public attitudes continue to evolve, there lies an auspicious opportunity for governmental bodies and health organizations to work in concert with community leaders to foster integrity and well-being within society.
Yet, it is essential to approach these improvements with caution. The reduction in alcohol consumption must not be perceived solely as a triumph; covert societal pressures that still glorify drinking can undermine any progress. Achieving a sustainable shift necessitates a comprehensive strategy encompassing education, community engagement, and a nuanced understanding of cultural significance pertaining to alcoholic beverages.
The Intersection of Identity and Consumption: Cultural Reflections
Alcohol consumption is more than a mere indulgence in beverages; it is a reflection of identity. The relationship that Russians maintain with alcohol forms an indelible part of their cultural narrative, where vodka often symbolizes resilience and camaraderie. Yet, the evolving perception surrounding drinking introduces complexities that extend beyond the scope of personal choice.
As society bears witness to shifting values—favoring moderation over excess—there arises an opportunity to redefine what it means to indulge responsibly. This transition engenders a new discourse around self-worth, personal responsibility, and collective values. The intersection of cultural identity and consumption necessitates deep reflection, allowing these evolving societal norms to coexist with, rather than replace, traditional beliefs.
Acknowledging the past while leaning into a healthier future presents a conundrum that challenges Russians to negotiate their identity in a globalized world. The evolution of alcohol consumption mirrors the societal shifts of a nation in flux, grappling with its cultural roots while forging pathways toward a future steeped in wellness and sustainability.
Conclusion: A Crossroads of Change
The trajectory of alcohol consumption in Russia is at a significant crossroads, marked by a burgeoning desire for change amidst an enduring cultural legacy. The diminishing proclivity for heavy drinking unveils an evolving mindset, embracing wellness while recognizing the historical implications of excessive consumption. As society navigates through this transformative period, attention to the nuances of cultural identity and public health initiatives remains imperative.
Ultimately, the shift in perspectives surrounding alcohol consumption holds the potential to reshape the social framework of Russia, inviting a more profound dialogue on identity, community, and well-being. By nurturing an informed and enlightened populace, the future promises a more resilient society that prioritizes health, sustainability, and inclusive practices, paving the way for an enriched cultural tapestry.