The advent of neurofeedback therapy marks a significant evolution in the landscape of psychological and cognitive treatments. With roots embedded in biofeedback, this technique represents an intersection of neuroscience and therapeutic practices, offering insights into the functioning of the human brain. Herein lies an exploration of neurofeedback therapy, inviting you to uncover its implications, applications, and challenges through a playful yet scholarly lens.
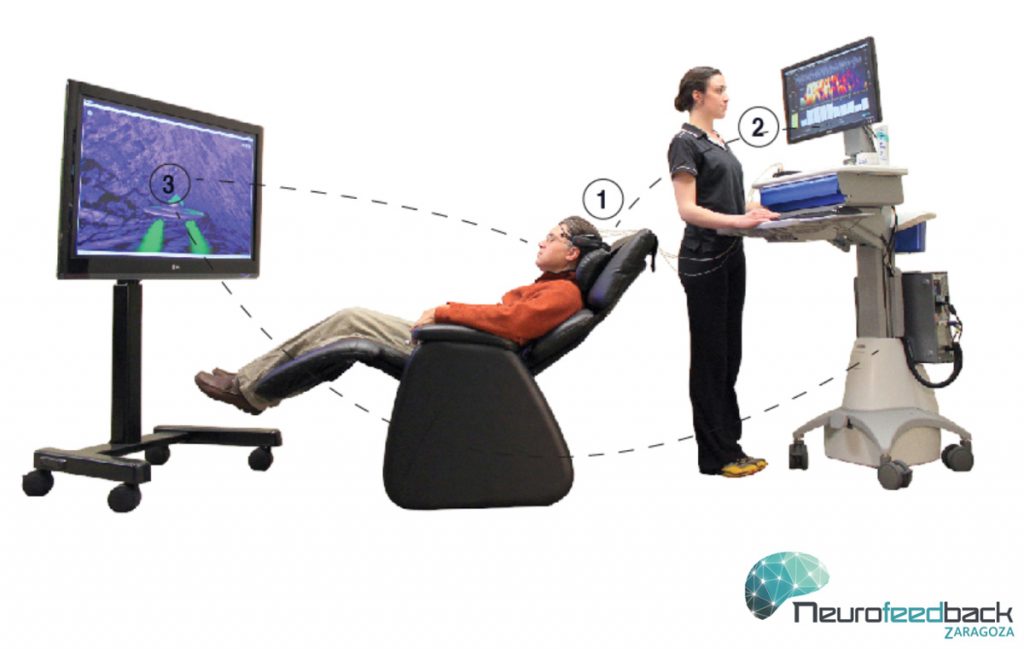
At its core, neurofeedback is a form of biofeedback that focuses specifically on the brain’s electrical activity. By providing real-time feedback on brainwave patterns, individuals can learn to self-regulate their cognitive and emotional states. The fundamental premise is simple yet profound: if one can observe their brain’s activity, they can modify it, potentially leading to improved mental health outcomes. This invites us to ponder a tantalizing question—can we truly harness the power of our minds?
Neurofeedback therapy, often described as a playful cognitive game, engenders a sort of cognitive alchemy by allowing participants to transform their mental states deliberately. However, the ramifications of such interventions beg for critical scrutiny. This therapy oscillates between the promising allure of self-enhancement and the perplexities of ethical considerations.
I. The Mechanisms Behind Neurofeedback
Understanding the mechanisms of neurofeedback requires delving into neurophysiology and cognitive psychology. The therapy utilizes electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brainwave frequencies—delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma—each associated with specific cognitive and emotional states.
The EEG sensors detect these brainwaves and relay the information back to the participant in an engaging manner, often through visual or auditory stimuli. For instance, a person watching a video game screen must rely on their conscious mental effort to alter the image based on their brain activity. The therapeutic implications of this feedback loop stimulate a sense of agency and empowerment. It posits an intriguing hypothesis: can individuals cultivate a heightened self-awareness of their mental processes through structured feedback?
This multifaceted approach has garnered attention for its applications across various mental health domains, including anxiety, depression, ADHD, and PTSD. Yet, while the potential for enhancement is considerable, so too are the concerns regarding its accessibility and ethical applications.
II. Applications and Efficacy of Neurofeedback Therapy
The versatility of neurofeedback therapy is both its strength and its Achilles’ heel. In therapeutic settings, practitioners often customize protocols to target specific conditions. For instance, studies have reported promising results in using neurofeedback to ameliorate symptoms of ADHD. By training individuals to increase their beta waves and reduce theta activity, the therapy has demonstrated a noteworthy capacity to enhance attention and self-regulation.
Moreover, research has shown its utility in treating anxiety and depression, where enhancing alpha activity can foster relaxation and mitigate negative affect. The playful challenge for participants lies in the self-regulation of their mental states, engendering a shared journey with the therapist that can strengthen therapeutic alliances.
Furthermore, neurofeedback therapy is finding its place in performance enhancement arenas, such as sports and the arts. Athletes and musicians alike are engaging in neurofeedback sessions to sharpen focus and cultivate peak performance states. However, this proliferation of applications evokes the question of commodification: Is the therapeutic process being repurposed for competitive gain rather than genuine mental wellbeing?
III. Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
The intersection of neurofeedback with ethical considerations merits profound contemplation. As the technology evolves, issues surrounding consent, access, and outcomes emerge prominently. The exuberant enthusiasm for neurofeedback can lead to commodifying its use, arguably detracting from the moral imperative of prioritizing patient welfare over profit.
Additionally, the regulatory landscape surrounding neurofeedback therapy remains murky. Unlike traditional psychological treatments, neurofeedback does not yet enjoy universal acceptance within medical communities. The skepticism that accompanies its legitimacy often raises concerns regarding professionals lacking adequate training or institutions exploiting neurofeedback’s allure without comprehensive understanding.
A further dimension to consider is the inclusivity of neurofeedback therapy. The cost and accessibility may restrict its benefits primarily to those with financial means—a disparity that runs counter to the principles of equitable healthcare. How can we ensure that neurofeedback therapy remains an accessible resource for all, particularly marginalized communities?
The future trajectory of neurofeedback therapy also hinges on ongoing research and technological advancements. The fusion of neurofeedback with artificial intelligence and machine learning could exponentially enhance its efficacy and customization. However, alongside this potential lies the necessity for rigorous scientific validation to substantiate claims of effectiveness and safety.
As neurofeedback continues to gain traction, it challenges conventional therapeutic paradigms. The playful interaction between brain and behavior invites us all to consider a fundamental rephrasing of our cognitive relationship: we are not merely passive recipients of our mental states; we are agents with the capacity to influence and mold our own neurological frameworks.
Ultimately, as we traverse the vast landscape of neurofeedback therapy, one must embrace a balanced perspective—cherishing the opportunities it presents while remaining vigilant against the ethical quandaries it entails. Neurofeedback therapy stands at the confluence of possibility and responsibility, beckoning us to engage in thoughtful dialogue and rigorous exploration. What role will you play in this evolving narrative? Embrace the challenge, for the journey towards understanding the self is as pivotal as the destination itself.